The Ivozio complex (Pognante et al., 1980) is part of the Eclogitic Micaschists Complex (EMC) of the Sesia-Lanzo Zone (SLZ). The SLZ (Fig. 1) is traditionally separated in two elements (Compagnoni et al., 1977; Dal Piaz et al., 1972): an upper element or "II Zona Diorito-Kinzigitica" (IIDK), comprising metapelites and metabasics with a dominant pre-Alpine metamorphic imprint under amphibolite/granulite facies conditions, and a lower element consisting of polymetamorphic metapelites, metagranitoids and metabasics, with Permian igneous bodies (e.g. Monte Mucrone, Val Sermenza gabbro). The lower element is further divided in three metamorphic complexes: the "Gneiss Minuti Complex" (GMC), showing a dominant Alpine metamorphic imprint under greenschist facies conditions, and the "Eclogitic Micaschists Complex" (EMC), showing a dominant Alpine imprint under eclogite facies conditions and the Rocca Canavese Thrust Sheet (Pognante, 1989a; Pognante, 1989b; Spalla and Zulbati, 2004) lawsonite-blueschists facies metamorphic imprint characterizes the P-retrograde exhumation path.
Figure 1. Location Map
a) Tectonic outline of the Alpine chain with the location of the Sesia-Lanzo Zone;
b) Simplified geological map of the Sesia-Lanzo Zone.
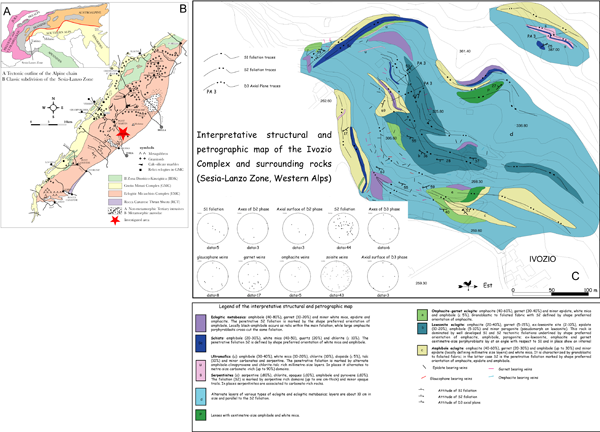
c) Interpretative structural and petrographic map of the Ivozio mafic-ultramafic complex (Austroalpine domain, Sesia-Lanzo Zone, Western Alps): field mapping by S. Racchetti, M.I. Spalla, M. Zucali and F. Zulbati Petrillo. Stereographic projections of main mesoscopic fabric elements.
The structural evolution of the EMC of the SLZ (Table 1) is accomplished during pre-Alpine times under granulite to amphibolite to greenschists facies conditions (Lardeaux, 1981; Lardeaux and Spalla, 1991; Spalla et al., 2005; Zucali, 2002; Zucali et al., 2002) and during Alpine times under prograde blueschists to retrograde greenschists, through eclogite facies peak conditions.
Table 1a. Structural evolution of EMC of the SLZ
| References | Pre-Alpine | Blueschists | Eclogite | Blueschists | Greenschists |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Relationships between deformation and metamorphism in the EMC of the Sesia-Lanzo Zone, according to the literature: (1) Gosso, 1977; (2) Pognante et al., 1980; (3) Passchier et al., 1981; (4) Williams and Compagnoni, 1983; (5) Hy, 1984; (6) Ridley, 1989; (7) Ildefonse et al., 1990; (8) Venturini et al., 1991; (9) Inger and Ramsbotham, 1997; (10) Zucali et al., 2002. | |||||
| (1) | D1 | D2 | D3 | ||
| (2) | D0 | D1 | D2 | D3 | |
| (3) | D0 | D1 | D2 | D3+D4 | |
| (4) | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 |
| (5) | D0 | D1 + D2 ----------> D2 | |||
| (6) | D1 | D2 | D3 | ||
| (7) | D1 + D2 ----------> D2 | D3 | |||
| (8) | D0 | D1 | D2+D3 | D4 | |
| (9) | D0 | D1+D2 | D3 | static | |
| (10) | pre-D1 | D1 + D2 + D3 | D4 | D5+D6 | |
The records of pre-Alpine and Alpine evolutions are richer within micaschists and gneisses. During pre-Alpine deformations a penetrative foliation was imprinted within metapelites marked by Crd + Bt + Pl + Kfs + Sill + Grt + Ilm and by Opx + Grt + Pl + Amp + Bt + Ilm in basic granulites (Lardeaux and Spalla, 1991) P - T estimates for the pre-Alpine evolution indicate 0.6 ≤ P ≤ 0.9 GPa and T = 700 - 900°C under granulite facies conditions, followed by an amphibolite facies stage (P = 0.3 - 0.5 GPa and T = 570 - 670 °C) and by a greenschist facies re-equilibration (P = 0.25 - 0.35 and T < 550°C) (Lardeaux and Spalla, 1991; Rebay and Spalla, 2001).
The Alpine evolution is characterized by polyphasic deformation under blueschist to eclogite facies conditions followed by retrogression under blueschist to successive greenschist facies conditions (Compagnoni, 1977; Compagnoni et al., 1977; Dal Piaz et al., 1972; Gosso, 1977; Pognante et al., 1980; Tropper et al., 1999; Zucali, 2002; Zucali et al., 2002). The eclogite facies stages occurred at P 2.1 GPa and T 650°C, as inferred by (Tropper and Essene, 2002) on the basis of Ky-occurrence as armoured inclusions in Grt-bearing amphibolites; during blueschists to greenschists facies retrogression km-scale folding of eclogitic foliation occurred, in places associated with a new penetrative foliation. Large scale shear zones developed during final stages of greenschists facies re-equilibration in central SLZ (Handy et al., 2005). Brittle-ductile faulting also occurred during the final stages of the Alpine evolution and assisted intrusion of andesitic dykes and igneous stocks (i.e. Biella-Miagliano and Traversella in Fig. 1).
Absolute age estimates and field relationships (see Table 1b for references and used methods) allowed to attribute an age 270 Ma to the granulite facies stage, an age 240 Ma to the amphibolite facies and an age 170 Ma to the greenschists facies metamorphism. Mineral ages ranging between 60 and 70 Ma have been related to the Alpine eclogite facies peak.
The Ivozio complex (Figure 1) includes eclogitic metabasics, eclogites, lawsonite-eclogites and scarce ultramafics that show layers of metapyroxenites and antigorite serpentinites; a primary igneous layering also exists (Pognante et al., 1980). All lithologies record penetrative Alpine metamorphic imprints, whereas pre-Alpine assemblages are scanty. Pognante et al. (1980) described a pre-eclogitic stage of deformation under blueschists facies conditions with extensive granular scale deformation; B1 and B2 deformation phases developed the main composite foliation and were associated with the wide development of eclogite facies assemblages within all lithologies; Lws growth was doubtfully attributed to B1 structures. B3 large-scale folds occurred under blueschists facies conditions; the Late Alpine evolution ended with a poorly developed stage under greenschists facies conditions. The metabasic protoliths of Ivozio complex have been dated by Rubatto (1998) at 355±9 Ma (see Table 1b). The lithologies of the Ivozio complex are mutually folded during eclogite to blueschist facies deformation phases, while a greenschist facies deformation refolds the main contact between the Ivozio complex and the surrounding paraschists and metagranitoids of the EMC (B3 deformation phase in Pognante et al., 1980).
Table 1b. Geochronological data for the SLZ
| PRE-ALPINE | ALPINE | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locality | Lithology/metamorphic stage | Method | Mineral | Age (Ma) | Reference | Locality | Lithology | Method | Mineral | Age (Ma) | Reference |
| SLZ Nord | metaporphyrites | U-Pb | Monazite | 448±5 | Romer et al. 1996 | Monte Mucrone (EMC) | Eclogite | SHRIMP | Zircon | 65±5 | Rubatto et al. 1999 |
| Ivozio Complex (EMC) | metagabbros | SHRIMP (sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe) | Zircon | 355±9 | Rubatto 1998 | Aosta Valley (EMC) | Micaschist | SHRIMP | Zircon | 65±3 | " |
| Cima di Bonze (EMC) | metagabbros | SHRIMP | Zircon | 350±4 | Rubatto 1998 | Cima di Bonze (EMC) | Mafic rocks | SHRIMP | Zircon | 68±7 | " |
| Monte Mucrone-Val Sermenza gabbro (EMC) | metaintrusive | U-Pb | Zircon | 293+1/-2 286-287 | Bussy et al. 1998 | Monte Mucrone (EMC) | Metaquartz-diorite | Rb-Sr | White Mica | 63±1.3 | Inger et al. 1996 |
| Corio-Monastero metagabbros SLZ | granulite facies metamorphism | structural relationships | - | ~270 | Rebay and Spalla 2001 | Monte Mucrone (EMC) | Eclogite | Rb-Sr | White Mica | 63±1.4 | " |
| SLZ | amphibolite facies metamorphism | structural relationships | - | =240 | Lardeaux & Spalla 1991 - Rebay & Spalla 2001 | Monte Mars (EMC) | Metapelite | Rb-Sr | White Mica | 63±1.5 | " |
| SLZ | greenschist facies metamorphism | structural relationships | - | =170 | Rebay & Spalla 2001 | Settimo Vittone (EMC) | Metapelite | Ar-Ar | White Mica | 64-66 | Ruffet et al. 1997 |
| SLZ | metasomatic stage/ veins | SHRIMP | Zircon | 221±14 | Rubatto 1998 | Lillianes-Fontainemore (EMC) | Metaintrusive/eclogite | Lu-Hf | Garnet and Pyroxene | 69.2±2.7 | Duchene et al. (1997) |