Textures and assemblages developed in the rocks affected by eclogite-facies deformation
During the high-pressure event, Grt1 in the felsic gneiss, developed rims of new garnet (Fig. 2; Grt2; Alm47-53, Prp21-30, Grs17-29, Sps1-2) as well as compositional changes near grain boundaries and fractures (Fig. 3). These peraluminous rocks also contain mats of intergrown, fine-grained aluminosilicate, opaque oxide, and rutile (Fig. 4). Within the mylonitic foliation, fractured grains and pressure shadows, Grt2, ilmenite, titaniferous magnetite, rutile, and small amounts of biotite and clinozoisite formed (Fig. 2; Camacho et al., 2009).
Mafic granulites preserve thin, randomly oriented needles of aluminosilicate, clinozoisite, and garnet (note: the mafic granulites contain no garnet that crystallized during the Musgravian Orogeny) that have grown inside plagioclase (Fig. 5), and may have formed by either of the following two reactions:
anorthite + H2O = clinozoisite + aluminosilicate + quartz
4CaAl2Si2O8 + H2O =
2Ca2Al3Si3O12 (OH) + Al2SiO5 + SiO2
and
anorthite = grossular + aluminosilicate + quartz
3CaAl2Si2O8 = Ca3Al2Si3O12 + 2Al2SiO5 + SiO2
Figure 3. Compositional maps showing the distribution of Fe, Al, Ti and Ca along grain boundaries and fractures.
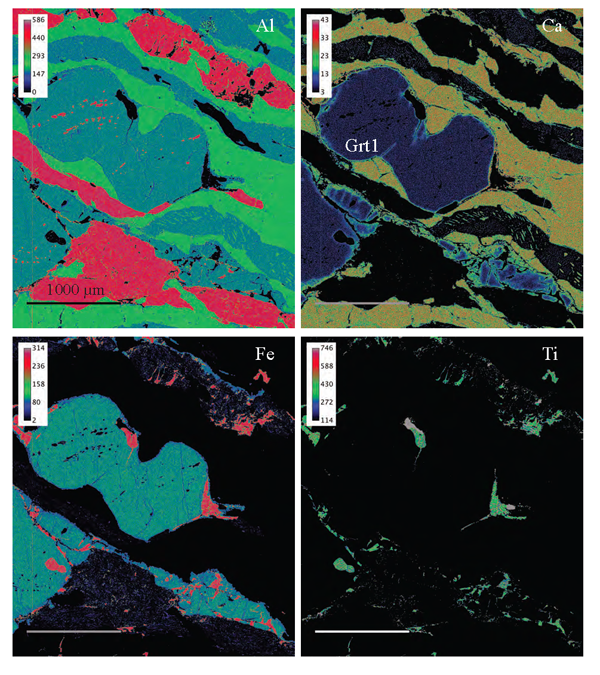
Compositional maps from X-rays collected in electron mircroprobe of the same area in Fig. 2a showing raw X-ray counts for Al, Ca, Fe and Ti. Relict granulite-facies garnet (Grt1) shows enrichment of Ca along rim and across fractures. Scale bar = 1000 µm. Rainbow colour scheme, with red and yellow representing higher concentrations than green, blue and black. Detailed colour scaling given in top left of each map.
Figure 4. Kyanite + opaque oxide + rutile mats
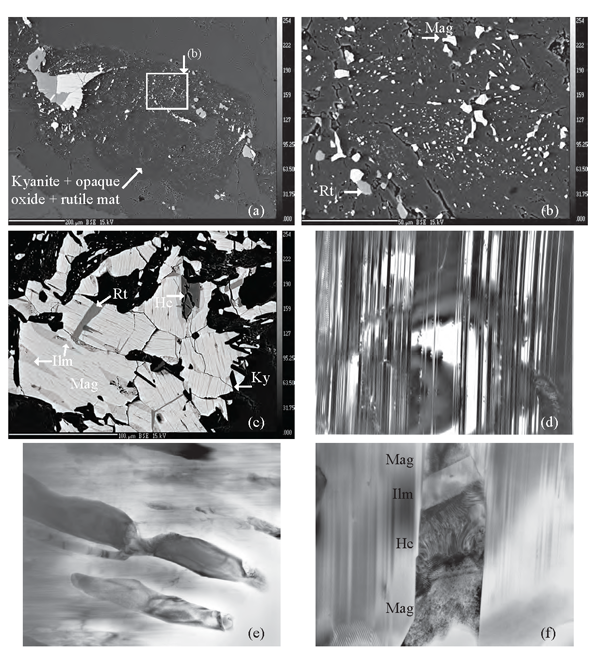
(a) Backscattered electron (BSE) images of the aluminosilicate-mat showing the general distribution of opaque oxides and rutile within kyanite. (b) Detail of Fig. 4a showing magnetite and rutile coexisting as fine blebs within kyanite. (c) BSE image showing magnetite (Mag) with ilmenite (Ilm) exsolution lamellae intergrown with rutile (Rt) and kyanite (Ky). Hercynite (Hc) partially enclosed by magnetite has a rim of ilmenite. Bright field TEM images of (d) Multiple twinning in kyanite. This twinning causes kyanite to have straight extinction under cross-polarized light. Base of photograph 2.32 µm. (e) Wormy intergrowths of dominantly magnetite (dark coloured) in twinned kyanite. Base of photograph 4.65 µm. (f) Close up of an intergrowth showing magnetite, with hercynite and ilmenite interpreted to be formed by exsolution, all enclosed in twinned kyanite. Base of photograph 1.00 µm.
Figure 5. New mineral growth resulting from plagioclase breakdown at high-pressure.
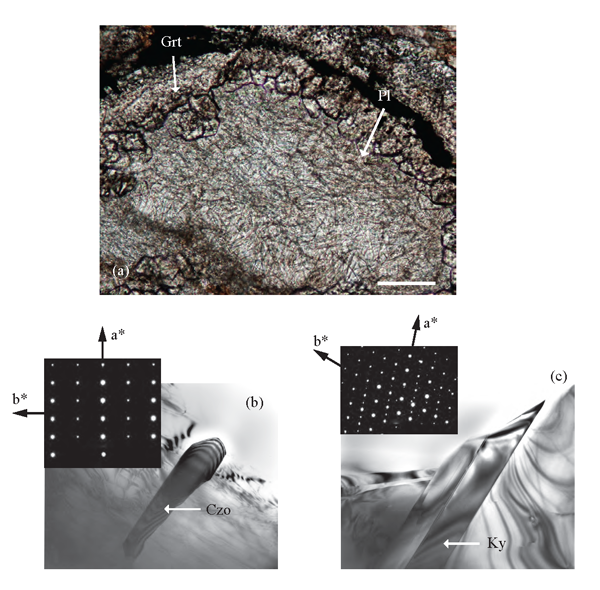
Eclogite-facies reactions of plagioclase in gneiss of mafic composition. (a) Coronas of garnet enclose plagioclase in contact with pyroxene. Clinozoisite and kyanite needles forming from the breakdown of anorthite component at high-pressure. See text for possible reactions producing these textures. Plane polarized light. (b) Bright field TEM image of clinozoisite (Czo). The trace of the needle is approximately parallel to (100). Base of photograph 2.32 µm. (c) Bright field TEM image of kyanite (Ky). The trace of the crystal is approximately parallel to (100). Note that is has a more uniform width than clinozoisite. Base of photograph 2.32 µm.
The fine-grain size of the aluminosilicates makes identification difficult using the optical microscope. Raman Spectroscopy and TEM were used to identify the aluminosilicates. In the felsic gneisses, sillimanite is preserved only as inclusions in Grt1 (Figs 2 and 6), and the mats are made up of kyanite and titaniferous magnetite (Figs 4 and 6), instead of sillimanite and ilmenite (Maboko et al., 1991), and appear to pseudomorph an earlier phase. Large area electron microprobe analyses of individual mats give compositions that represent an aluminosilicate with ~2 weight percent FeO and indicate that the phase being replaced was most probably sillimanite. Sillimanite typically contains ~1% Fe and, as the replacement appears to be isochemical, the growth of titaniferous magnetite may result from Fe not being incorporated into the more densely packed structure of kyanite. Tiny aluminosilicates in the plagioclase of the overprinted mafic granulites have also been identified as kyanite (Fig. 5).
Figure 6. Raman spectra, showing lattice vibration modes
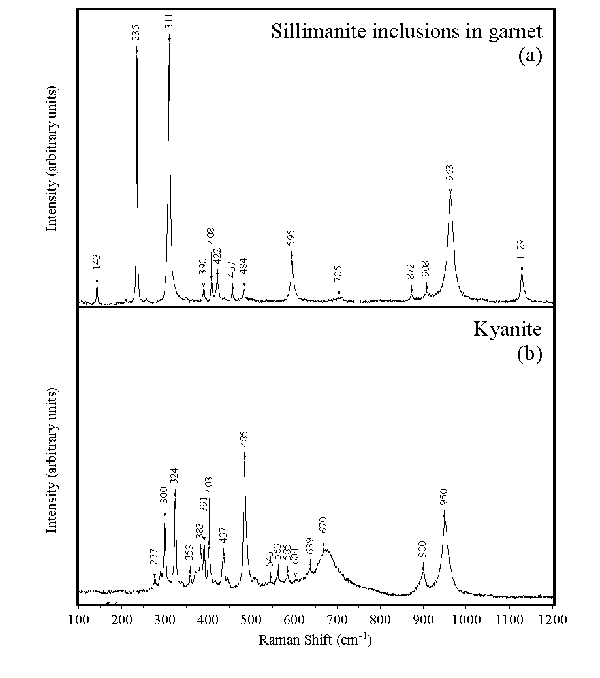
(a) the sillimanite inclusion in granulite-facies garnet (Grt1) shown in Fig. 2b, and (b) kyanite in the aluminosilicate + opaque oxide mats.