Myrmekite in Deformation Zones
|
Click image to enlarge |
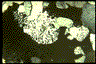
55. Myrmekitic intergrowths on K-feldspar
- The distinctive, cauliflower-texture of myrmekitic replacement reaction is evident
on the margins of a K-feldspar grain (black, lower left of image) from deformed adamellite
of the alpine Maggia Nappe, Ticino, Switzerland. Deformation was at epidote-amphibolite
facies. Recrystallized quartz grains fill the upper right part of the image. The
reaction of K-feldspar to plagioclase and quartz results in a volume decrease and
is favored on high normal stress sites around the grains.
|
|
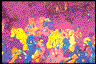
56. Recrystallized myrmekitic intergrowths on microcline - Relict myrmekitic quartz/oligoclase intergrowths are present along the foliation-parallel
edge of this large microcline crystal (upper half of image) from the Ponaganset augen
gneiss in the Hope Valley shear zone of eastern Connecticut. This microcline grain
is over 5 cm long and has well-developed tails of recrystallized K-feldspar (not
illustrated) parallel to the weak foliation and strong mineral lineation, which are
aligned horizontal to the image. Deformation occurred at temperatures of 440°-445°C.
Quartz relict vermicules (small, bright blue grains, all the same lattice orientation)
tend to be subrounded near to the microcline host crystal but are more polygonal
in outline with distance from it, toward the bottom of the image. The oligoclase
forms polygonal, straight-sided grains of random orientation, also indicating significant
post-formation recovery. Compare the morphology of these myrmekitic intergrowths
with those of image # 55, which shows the more classic bulbous
vermicular texture.
|
|
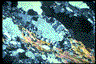
57. Myrmekitic intergrowths on K-feldspar - Myrmekitic
intergrowths here occur on the margins of a K-feldspar grain between S-planes in
an S-C mylonite from the Santa Rosa Mylonite zone in the Eastern Peninsular Ranges
of southern California. S planes are oriented from top left to lower right, and C-planes
are not visible in this image. Deformation was in the temperature range of 450°-550°C.
The K-feldspar grain in the center of image is bordered by biotite and quartz ribbons
with some muscovite and recrystallized feldspar grains. Myrmekitic intergrowths of
oligoclase and quartz are only observed on the two sides of the K-feldspar grain
that parallel the S-planes, which face the shortening direction. The reaction of
K-feldspar to plagioclase and quartz is volume-reducing and is favored on high normal
stress sites around the grains. Myrmekites do not occur on the two ends of the K-feldspar
that parallel the extension direction, where there are recrystallized new, equant,
K-feldspar grains.
|
|
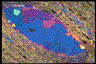
58. Myrmekitic intergrowths on K-feldspar - This example
of myrmekite development occurs in a mylonitic granite from the Catalina metamorphic
core complex of Arizona. Foliation is oriented top left to bottom right. The K-feldspar
porphyroclast sits in a matrix of fine-grained white mica, epidote, quartz and iron
oxides. Reaction to myrmekite is apparent along the uppermost margin of the K-feldspar.
Click here to view Flash animation in a new window.
|